Adoption of Blockchain Technology in the Workplace: Opportunities and Challenges
The adoption of blockchain technology in the workplace is a growing trend that promises to transform numerous industries by improving transparency, security, and efficiency. Blockchain, a distributed ledger technology, was first designed as the foundation for cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. However, its potential is far-reaching, with disruptive possibilities for data management and transaction processing in a variety of disciplines (Nakamoto 2008).
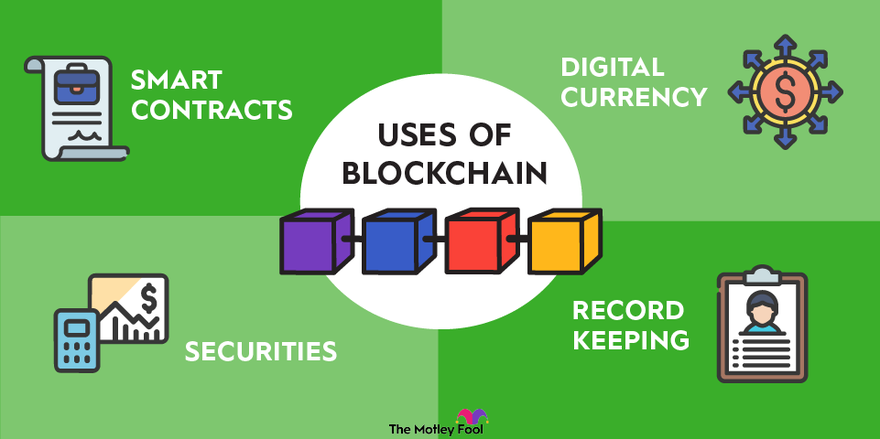
One of the most significant benefits of blockchain in the workplace is its ability to conduct safe and immutable transactions. According to Swan (2015), blockchain's decentralization eliminates the need for a central authority, minimizing potential points of failure and boosting resilience to fraudulent activity. This makes it an appealing choice for businesses like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management, where security and transparency are critical.
Furthermore, blockchain can significantly improve efficiency within the workplace. As Tapscott and Tapscott (2016) argue, blockchain enables real-time, automatic transactions that can streamline business processes, reduce redundancies, and cut costs. For example, smart contracts self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code can automate routine tasks and agreements, thereby speeding up operations and reducing the likelihood of human error (Christidis and Devetsikiotis, 2016).
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Blockchain_final-086b5b7b9ef74ecf9f20fe627dba1e34.png) |
However, the use of blockchain also raises various problems. Technical limitations, such as the need for enormous computer capacity and the complexity of blockchain programming, represent significant challenges (Zheng et al., 2017). Additionally, regulatory ambiguity and a lack of standardization might hamper implementation, as organizations must navigate a complicated web of legal and compliance challenges (Catalini and Gans, 2016).
 |
In conclusion, while blockchain technology brings tremendous benefits to the workplace, like higher security, increased efficiency, and improved transparency, it also comes with issues that need to be addressed. Organizations considering its implementation must assess the technological and regulatory challenges against the possible benefits. As this technology continues to grow, it will certainly become a more vital component of the workplace across numerous industries.
Conclusion
In summary, blockchain technology offers varied applications in the workplace that can address common business difficulties, boost operational efficiency, and promote creativity. For MBA students aspiring to lead in the business world, knowing and harnessing blockchain's potential could be vital to unlocking new opportunities and gaining strategic advantages.
References
Nakamoto, S. (2008) ‘Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.'
Swan, M. (2015) Blockchain: A Blueprint for a New Economy. O'Reilly Media.
Tapscott, D., and Tapscott, A. (2016) Blockchain Revolution: How the Technology Behind Bitcoin is Changing Money, Business, and the World. Portfolio.
Christidis, K., and Devetsikiotis, M. (2016) ‘Blockchains and Smart Contracts for the Internet of Things’, IEEE Access, 4, pp. 2292-2303.
Whiteboard Crypto. (2021) What is Blockchain? Animated + examples. https://youtu.be/kHybf1aC-jE?si=ieIuQu14h0wwsYqb (Access Date: 10 03 2023)
Whiteboard Crypto. (2021) What is Blockchain? Animated + examples. https://youtu.be/kHybf1aC-jE?si=ieIuQu14h0wwsYqb (Access Date: 10 03 2023)
Zheng, Z., Xie, S., Dai, H., Chen, X., and Wang, H. (2017) ‘An overview of blockchain technology: Architecture, consensus, and future trends’, in 2017 IEEE International Congress on Big Data (BigData Congress), pp. 557-564.
Catalini, C., and Gans, J.S. (2016) ‘Some Simple Economics of the Blockchain’, MIT Sloan Research Paper No. 5191-16.
Comments
Post a Comment